Doxycycline Tablet Size:
Image source: Drugs.com
Doxycycline systemic 100 mg
(blue/tablet/ imprint: West-ward 3142)
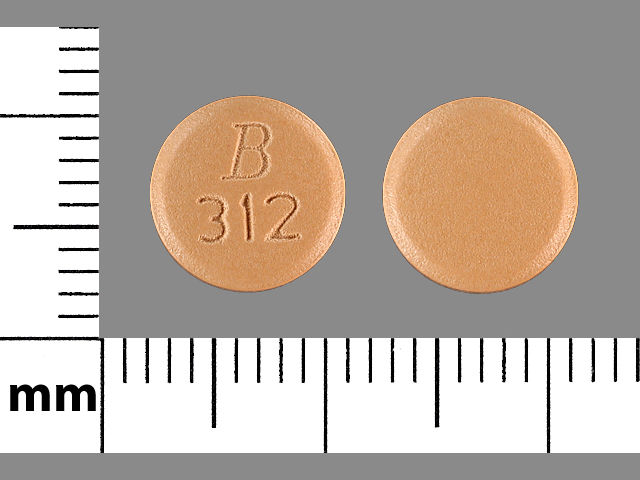

Image Source: Drugs.com
Doxycycline systemic 100 mg
(peach//imprint: B 312)
Overview:
Doxycycline is a drug created to inhibit bacterial growth by preventing bacteria from multiplying. More specifically, the antibiotic treats infections by preventing bacteria from producing the proteins it needs to survive and consequently inducing death. Due to these properties, it reduces the number of bacteria on the skin surface and can work against malaria-inducing parasites.
Medical Uses:
It is believed to have anti-inflammatory effects and is mainly used for treating bacterial infections including but not limited to acne, respiratory/urinary tract infections, gum disease, chlamydia, syphilis, and gonorrhea. It can also be used as a prevention measure for malaria along with treating diseases caused by lice, mites, or ticks. In general, the drug works best for skin and dental infections, along with STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
Side Effects May Include:
Headache, nausea, joint or back pain, or a rash
Sinus congestion
Calcium complexes developing in bone-forming tissues (can affect growth rate in young children)
Permanent tooth discoloration
Diarrhea
Skin sensitivity
Hives
Blistering
Decreased appetite
Possible allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
If any of these effects worsen, tell your doctor immediately.
Paradoxical Reactions (reactions that contradict doxycycline effects on the body)
Inflammation with or without pus formation of the infected area
Drug Interactions:
Medicines that interact with doxycycline can increase or decrease its effects, how long it works, lessen or heighten side effects, or decrease the anti-inflammatory effects the antibiotic has on the body. If the drug you are currently taking interferes with doxycycline you may need to stop taking that type of medication temporarily. Common medications that interfere with doxycycline are mentioned below:
Calcium supplements
Multivitamins
Iron supplements
Bismuth subsalicylate
Oral contraceptives
Warfarin
Penicillin
Please note that the list above does not mention all types of medication that may interact with doxycycline. Be sure to consult your healthcare provider on any drugs you are taking prior to consuming doxycycline.
Doxycycline Should Not Be Consumed If You Have The Following Conditions:
Liver or Kidney problems
Lupus or another autoimmune disease
Oesophagitis (inflamed food pipe)
Myasthenia gravis
Pregnant or breastfeeding
*If you are a child of 8 years or younger, you should not be taking doxycycline unless you have been exposed to inhalational anthrax, rickettsia infection, or have been prescribed it by a doctor.
Dosing Info:
You should consult your doctor on the dosing schedule you should follow, however the following is the typical dosing schedule provided by Mayo Clinic if you are using the medication to treat an infection.
For oral dosage forms (capsules, suspension, syrup, tablets):
For infections:
Adults—100 milligrams (mg) every 12 hours on the first day, then 100 mg once a day or 50 to 100 mg every 12 hours.
Children 8 years of age or older weigh 45 kilograms (kg) or more—100 mg every 12 hours on the first day, then 100 mg once a day or 50 to 100 mg every 12 hours.
Children 8 years of age or older weighing less than 45 kg—The dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. The dose is usually 4.4 mg per kg of body weight per day and divided into 2 doses on the first day of treatment. This is followed by 2.2 mg per kg of body weight per day, taken as a single dose or divided into two doses on the following days.
Children up to 8 years of age—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor.
Citation:
“Doxycycline: 7 Things You Should Know.” Drugs.Com, www.drugs.com/tips/doxycycline-patient-tips Accessed 7 June 2023.
“Doxycycline (Oral Route) Side Effects.” Mayo Clinic, 1 May 2023, www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/doxycycline-oral-route/side-effects/drg-20068229?p=1
NHS Choices, www.nhs.uk/medicines/doxycycline/who-can-and-cannot-take-doxycycline/#:~:text=have%20kidney%20or%20liver%20problems,that%20causes%20severe%20muscle%20weakness Accessed 7 June 2023.

Comments